Internal ant anatomy
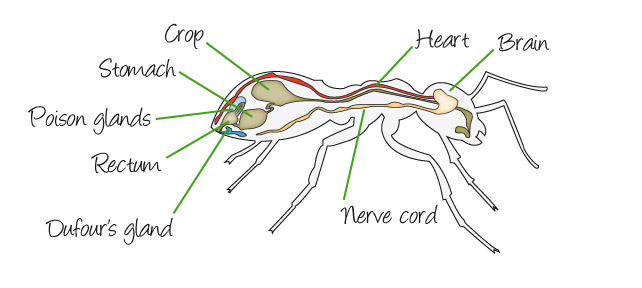 Brain – Allows the ant to remember, think and react to its environment.
Brain – Allows the ant to remember, think and react to its environment.
Heart – Shaped like a tube running through the ant, it surrounds the internal organs with a colourless blood.
Nerve cord – sends electronic messages through out the ants body, helping coordinate movement.
Crop – holds the ants social food it will share with the colony.
Stomach – where the ant digests its own food with acids.
Rectum – holds the waste products which will be deposited in the colonies designated waste area.
Poison glands – holds formic acid, which is sprayed and or injected as a defensive or attacking system.
Dufour’s gland – is believed to partly be involved with the production of chemicals that guide other ants and perhaps the attraction of mates.
